The transition to an online focus group format is the most recent innovation of the focus group. The Internet has made it possible for people from all over the world to come together online using chat and web conferencing technology. removing travel expenses and other logistical issues related to conventional face-to-face focus groups.
In this article, we will go through the concept of online focus groups and review some examples of this method.
What is an online focus group?
Online focus groups are essentially groups of participants (often 8–10) who are encouraged to discuss and debate a certain topic online. Although traditional focus group studies still have a place in the realm of qualitative research for some projects, many can be relocated online, with research benefiting from the convenience, time, and cost savings, as well as being helpful for respondents who are geographically dispersed.
Participants can express their opinions, ideas, and responses to questions much as in conventional, in-person focus groups.
Important similarities to conventional focus groups include:
- In order to foster a rich conversation within the forum, participants also respond to each other's answers.
- To engage in this type of qualitative research, participants must still pass an initial screening and be certified.
- With the exception of the venue and administration of the focus group, much of the essential process elements are the same.
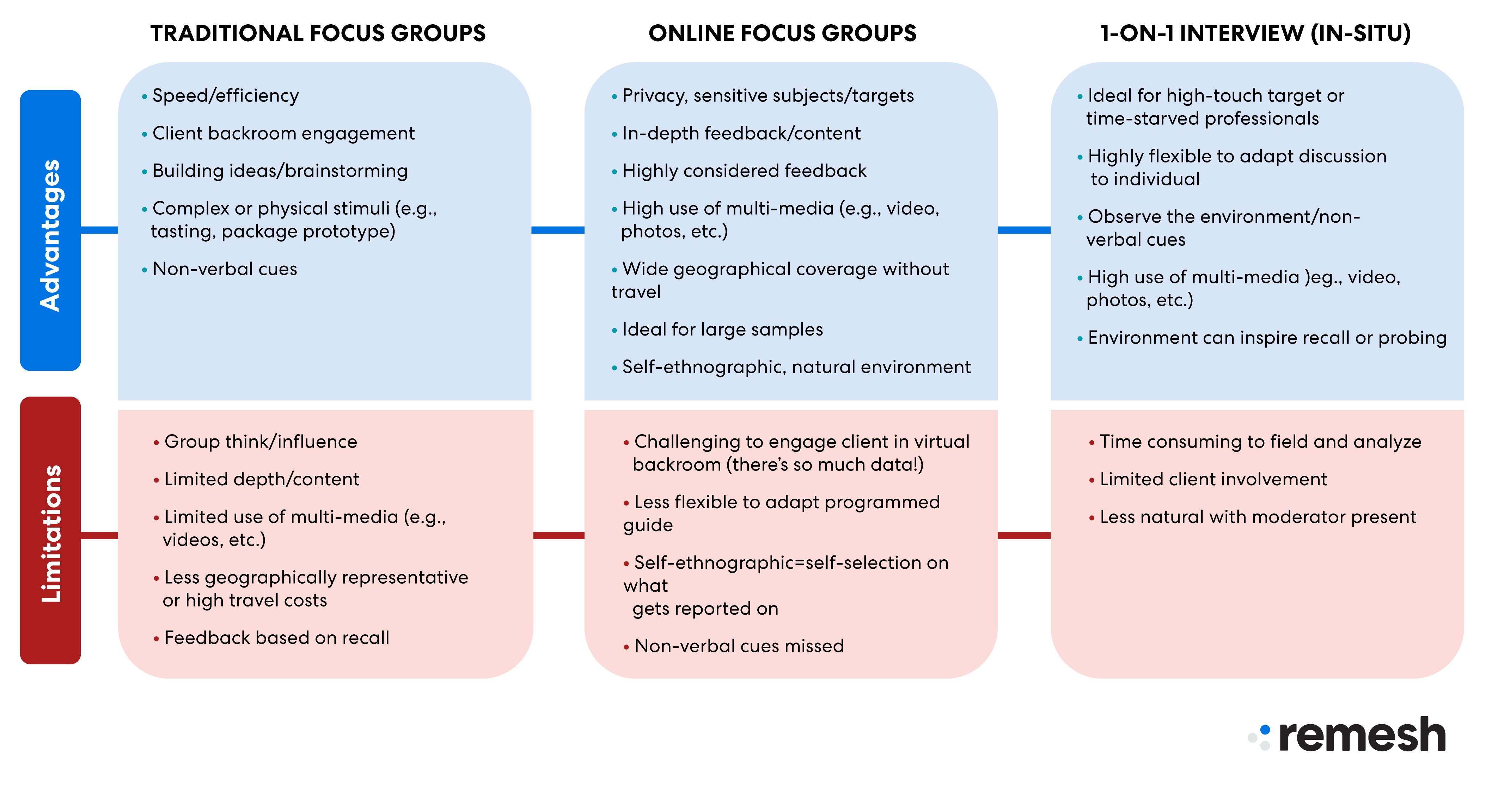
There are two kinds of online focus groups:
- Chat-based focus groups
- Webcam and audio-based focus groups.
Chat-based focus groups: These platforms are a fantastic alternative when simplicity and immediacy are important considerations. The technical needs are straightforward.
Participants' total time commitment is frequently 60 to 90 minutes or less. If the primary purpose is to understand top-of-mind reactions, analysis can be a quick procedure.
Webcam-based focus groups: Real-time platforms where the moderator and participants may see and hear each other while having discussions and reviewing stimuli. At the same moment, everyone gathers, sessions typically run 1.5 to 2 hours, and researchers may see and hear what participants are saying.
When should you use online focus groups?
When a rich insight is required, a focus group - online or offline - is an excellent form of qualitative data collection. This could be to probe deeper into issues previously identified through a quantitative study, to test products, concepts, or marketing materials, or to generate an initial picture of an unknown target group.
You may also be interested in: Seven consumer research methods; 2022 version
A focus group's goal is to establish a discussion among a group of participants regarding a specific research topic. Focus groups, as opposed to one-on-one interviews, allow group members to engage with and influence one another. While traditional focus groups are held in person, there are several advantages to conducting this research online.
Advantages and disadvantages of online focus groups
This market research methodology has its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
Geographical Independence
When deciding to conduct in-person focus groups, researchers and stakeholders must choose a few cities to which they can travel and which have a population of their target audience to recruit. This (rather arbitrary) selection means that the insights are acquired from residents of these specified cities, removing any randomness from the sample. Online focus groups enable research to be conducted nationwide or globally, depending on the brand's target audience.
The nearest online equivalent
Online focus groups are the most similar to in-person focus groups. While the basics of in-person focus groups include gathering a group of individuals in a room and having a moderator lead a discussion. The basic structure of online focus groups is the same: a group of participants and a moderator guiding a discussion.
Improved Efficiency
Since the travel involved, in-person focus groups take longer, researchers, moderators, and stakeholders all go to the location of in-person focus groups. Participants will be recruited locally and will be required to visit the site (by car or public transport). Online focus groups are far more efficient because researchers, moderators, stakeholders, and participants may all participate from the comfort of their own homes or offices.
Deeper Data
This benefit is not guaranteed, but there is an argument that participants are more relaxed at home and will provide more honest and open responses. Any factors, such as being in a focus group facility or in person with other participants, may be daunting and cause some individuals to remain mute.
Reduced Costs
Online focus groups are a less costly option than in-person focus groups. Facility hire and travel are two of the most expensive aspects of focus groups. There is no need for a facility or travel because there is no requirement to be in-person. Travel for the moderator and observers can be costly because you must pay for a hotel, flights, vehicle service, and meal costs.
Disadvantages
Unstable Internet
Even if we live in 2022 and have fast internet, there may still be instability. This variation may cause speakers to pause in the middle of sentences, including the moderator. Another justification for tech support being there during the entire session is this. If this occurs, tech support may attempt to assist in reconnecting the user.
Long lag times are another problem that a slow or unstable internet might bring about. There are occasions when the sound is present but the video is silent. Although not as serious a problem, this can make transitions challenging and frequently results in people speaking over one another. When the video or audio lags, it may appear to the moderator that someone has ceased speaking.
Distraction
Participants are frequently far more distracted when they are online, in contrast to how much more at ease they are at home. They are logging in using their home address. Even when we encourage them to eliminate all sources of distraction, there may still be a family member or pet that needs their attention or forces them to take a brief break from their computer.
Technical Challenges
When participating in online focus groups, participants frequently use new technologies. The learning curve may make it difficult to download the software, log in, or set up. Therefore, before entering the session, it is crucial to have technical support for every participant. Incentives for early log-on times are also frequently recommended since they encourage people to join the group early and work out any problems with the technology.
Best practices of online focus groups
To perform online qualitative research, you must have the proper tools in order to gain the necessary insights. The following are some best practices for running an online focus group:
The size of online focus groups, similar to offline focus groups, should be between 7-10 members to yield the strongest insights while being manageable.
Sampling and bringing the correct people to an online focus group is critical. To ensure excellent data collecting quality, use correct sampling methodologies and bring in a mix of customers and promoters.
Also read: How Consumer Insights Help Your Business Grow
Preparation is essential because online focus groups are held remotely. Time, tool, participants, questions, and data analysis should all be tracked in order to achieve your study objectives.
A platform for online focus groups is the tool you use and is the most important component of the experiment. Use a research platform that meets your study objectives and provides the freedom to examine and publish data.
As a moderator, pick what role you want to play in the research study to get the most out of the respondents and drive conversations in the most insightful way.
Immediate Rewarding should take place right after the conclusion of the study discussion. Typically, research participants must pay at the end of an in-person interview or focus group.
Allow mobile participants (with certain needs) to connect using their smartphones. Smartphones are often simple for average consumers to use and an excellent tool for participating in the video focus groups.
Allowing extra time for technical difficulties is important. It's also crucial to ask individuals to arrive 5–10 minutes early. By planning for this extra time, the participant and moderator can deal with any last-minute technological difficulties. This will guarantee that the discussion of the research may begin straight away without taking up too much of the given time for the moderator and participants.
Examples of online focus groups
In order to solve a problem, focus groups are occasionally organized. Let's say, for instance, that certain employees are exerting more effort than others, which is causing increasing levels of annoyance. But they are still getting worse outcomes.
A focus group could be formed comprising staff members, including managers and employees, to talk about the issue. They might eventually decide to invite experts to the gathering.
A problem-solving focus group should adhere to the following procedures for optimum results:
- Determine the issue and explain it.
- Examine the issue.
- Establish standards.
- Put forward potential fixes.
- Discuss the answers.
- Pick the best option(s).
- Activate the solution.
- Hold follow-up meetings to assess if the problem was resolved by the solution.
Another example is an airline that aims to create a better product is another instance of a company that actively uses online focus group research techniques for in-depth monitoring. The airline can gather and analyze attitudes and purchasing decisions via interactive groups with a small group of customers and brand advocates to improve their goods and services.
Also Read: Differences Between Market Research and Consumer Insights Research
A clothing company that managed market research to gauge consumer perceptions throughout the launch of new products is an example of a focus group study. Focus groups can now be conducted online with the aid of online focus group software, allowing businesses to continue gathering consumer and audience insights and deciphering buyer intent and decisions.
A focus group could serve as a representative sample of a population in market research. For instance, a political party might be curious about the responses of young adults to various policies. Market researchers would then present their findings to their client after listening in on conversations among young adults on those policies. A newspaper, a think institute, or a political party could be the customer.
By switching to online methods, any company, researcher, or organization that currently conducts offline focus groups can serve as an example of an online focus group.
Final words
Focus groups might be physical or online, but their primary purpose is to represent a broader population through the group members' thoughts and reactions, which should mirror the perspectives of that population.
Without a question, online focus groups are the way of the future for research. It has a high ROI, is incredibly powerful, and is simple to manage. Make your focus groups available online to fully utilize the advantages of online qualitative research.